Intracytoplasmic Injection
We attend cases of male infertility.This technique is used when common causes of male infertility are found in the seminogram study. The process is performed when the sperm is injected into the cytoplasm of an egg.
In our laboratories the fertilization of the ovules is carried out immobilizing them by aspiration to micro inject the spermatozoon in the center of each egg.
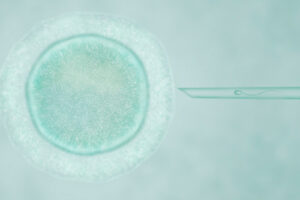
Intracytoplasmic Injection Procedure
The steps are similar to those of a conventional IVF treatment, with the difference that the insemination of the ovules is done by micro injection; that is, the sperm is artificially introduced into each ovum obtained.
Who are candidates for this treatment?
- Due to difficulty with normal ejaculation.
- After performing several cycles of IVF without positive results.
- When female infertility or ovulation problems occur
- When the man has had a vasectomy.
- When having low mobility sperm or bad morphology.
- When cryopreserved samples already exist.
Our process
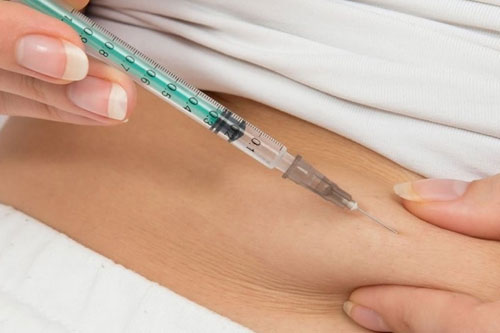
It consists of inducing a multiple ovulation using hormonal medication. This method allows us to anticipate the exact moment of ovulation as well as the correct maturation of the ovule to be inseminated.
1. Ovarian Stimulation

It is the procedure by which the mature ova (measured between 15 and 18 mm) of the patient are extracted for fertilization in the laboratory. It is performed by needle puncture guided by transvaginal ultrasound. The patient should be sedated (asleep).
2. Puncture, capture and aspiration.
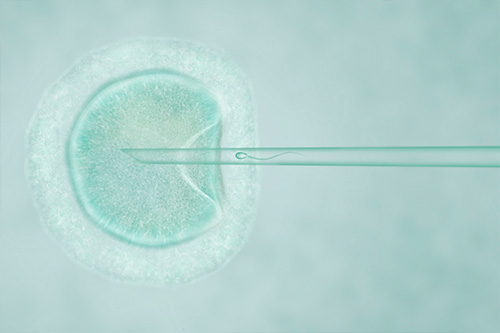
Process by which the egg is fertilized by the sperm for the creation of the new being (embryo), this process can be done spontaneously (FIVTE) or by injecting a sperm into each extracted egg (ICSI).
3.Fertilization of ovules.

Once the oocyte is fertilized, its development is observed in the laboratory until it is in optimal conditions for its transfer to the maternal uterus.
4. Embryonic culture.

When the embryo is at its best to be implanted in the woman's uterus it is placed inside the body of the uterus to begin its development and therefore pregnancy.
5. Embryonic transfer.

The freezing of high quality embryos is recommended for future attempts, if pregnancy is not achieved, since the success of this treatment always depends to a great extent on the age of the patient.